
December 9, 2024 by WindowRama
How to Choose Energy-Efficient Windows
Selecting energy-efficient windows is easier when you know what factors to focus on. This guide from Andersen Windows breaks down what you need to consider, from window types to glass coatings, so you can choose the best option for your home and climate.
Do New Windows Help With Cooling & Heating?
The U.S. Department of energy estimates that windows are responsible for 25%-30% of heating and cooling in residential homes. Preventing energy loss, especially if your windows are aged out or worn down, can provide some significant savings to your heating and cooling bills.
Over time, age related deterioration can lead to a loss in energy efficiency. Seals can break down causing ‘leaks’ in them. Some windows have argon gas, a colorless and non-toxic gas that offers strong insulation properties which are lost over time. In other cases, weather-stripping along the window can wear down causing a looser seal, leading to less efficiency. Depending on the age of your windows, energy efficiency standards may have changed meaning that newer, energy efficient certified windows simply offer better performance. Installing new energy saving windows can help to lower energy costs and reduce heat transfer by adhering to more modern Energy Star guidelines.
What Makes Windows Energy Efficient?
It likely doesn’t surprise you that different window types offer different levels of energy efficiency based on the tightness of the seals they provide. Different window types have a different number of sashes (the movable part that surrounds and holds the glass in place). The more parts that move, the more openings and the looser seal a window may have.
Casement and awning windows only have a single sash. Other window types, such as a double hung, have two sash with two movable sections. Therefore, a picture window with no sashes (because they do not open) are the most energy efficient!
Fixed windows, like picture windows, are the most efficient since they don’t open!
Casement, awning, and picture windows are more energy-efficient than double-hung windows because of their tighter seals.
Most Energy Efficient Window Type
-Casement, awning, and picture windows are more energy-efficient than double-hung windows because of their tighter seals.
-Fixed windows, like picture windows, are the most efficient since they don’t open.
Understand Glass Options
There are three types of glass options available to choose from:
- Single-pane glass: Found in older homes but lacks insulation.
- Double-pane glass: Offers better insulation with an argon-gas blend between panes.
- Triple-pane glass: The most efficient option, recognized by ENERGY STAR® and ideal for extreme climates.
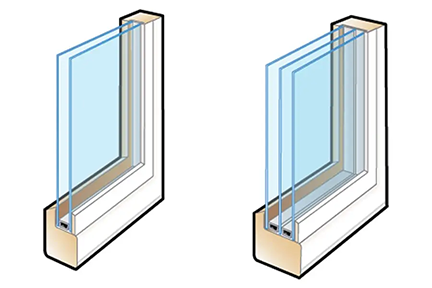
As you may expect, windows become more expensive based on the number of layers of glass that it uses. However, more window layers also means longer lasting. On average, a triple pane glass window can last as long as 30 years. A double pane window may last up to 20 years, and a single pane glass window lasts at most around 10 years before it starts degrading. Although triple pane glass is ideal for extreme conditions, you may find that the increased lifespan justifies the increased cost. Triple pane windows can also reflect about 97% of energy if paired with the right window types (casement or awning).
If your windows are older than 30 years, it should be time to consider replacement windows.
Consider Glass Coatings
Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings reflect or absorb heat based on your climate. Options include:
-SmartSun™: Reduces UV rays and protects furnishings.
-PassiveSun®: Captures warmth in colder climates.
-HeatLock®: Retains heat in northern regions.
-In warm climates, coatings like Sun glass help keep your home cool.
Know Performance Metrics
-U-Factor: Measures heat retention—lower numbers mean better insulation.
-Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC): Indicates how much solar heat a window allows—lower numbers are better in hot climates.
Frame Materials
Frames offer more than just curb appeal. Vinyl frames, for example, offer stronger insulation than all-wood windows. The different types of window frames may also be more resistant to decay over time meaning that they won’t lose energy efficiency as quickly.
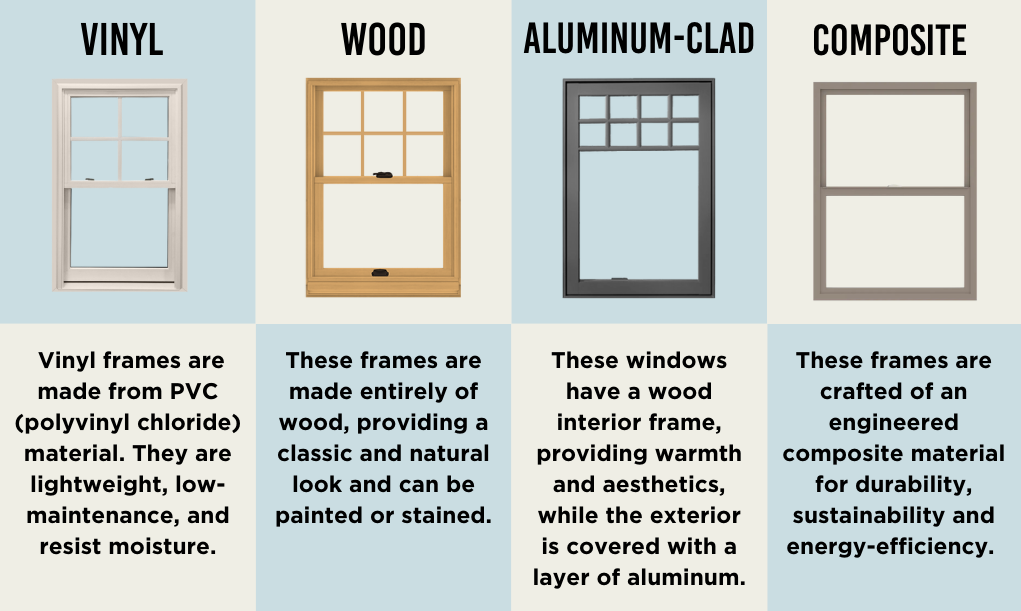
Aluminum frames conduct heat making them poor insulating material. Aluminum frames are best as a budget option or where energy efficiency is not a concern.
Wood frames have higher maintenance requirements making them more susceptible to wear and tear over time which can lead to a loss in energy efficiency. Wood frames generally are best for aesthetic choice, customizability, and longevity as they can last as long as 30 years if they are maintained properly.
Composite frames are very stable and while they offer comparable insulation to wood windows they are less susceptible to damage over time from warping or sagging.
Vinyl frames are made from hollow materials which allows them to be filled with insulation that makes them a stronger choice than wood, composite, and aluminum. Additionally, they have strong resistance against UV which prevents wear and tear and a high ability to resist damage from moisture meaning they maintain their energy efficiency for longer. Vinyl has a high ‘r’ value meaning it does a good job of preventing heat from entering on hot days and leaving on cold days.
Fiberglass frames are considered the strongest when it comes to durability, energy efficiency, and longevity. They have air cavities that can be filled with insulation but their superior performance generally comes at a higher price when compared to other frame materials.
Additional Tips
-Grilles and Breather Tubes: Grilles touching the glass reduce efficiency, but designs like Andersen’s energy spacer bars avoid this. High-altitude homes may require breather tubes, which slightly impact efficiency, but can be offset by other choices.
-Look for Certifications: ENERGY STAR® and NFRC labels indicate tested and verified energy performance.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows
–Save Money: ENERGY STAR-certified windows can reduce annual energy bills by 12% or more.
–Improve Comfort: Reflect heat in summer and retain warmth in winter.
–Increase Home Value: Energy-efficient windows offer an average return on investment (ROI) of 69.5%.
–Environmental Impact: Reduce your carbon footprint and extend your HVAC system’s lifespan.
–Tax Incentives: ENERGY STAR-certified windows may qualify for a federal tax credit of up to 30% of the cost (up to $600) through 2032.
By choosing the right energy-efficient windows, you can save on bills, enhance your home’s comfort, and even increase its value—all while being environmentally responsible.